The red ghost would chase them down from behind following Pac-Man throughout the maze, blue would base his actions on the red one as he moved to areas that would corner Pac-Man as he was being chased by red, next-up is the pink ghost who is the smartest (with her trying to think ahead and predict where the player might be), and lastly is orange who is designed to do their own thing wander about, and sometimes choose to not even attack the player, in order to really make these enemy ghosts seem more like actual characters that can shine through the game's retro graphics than just being all the same.
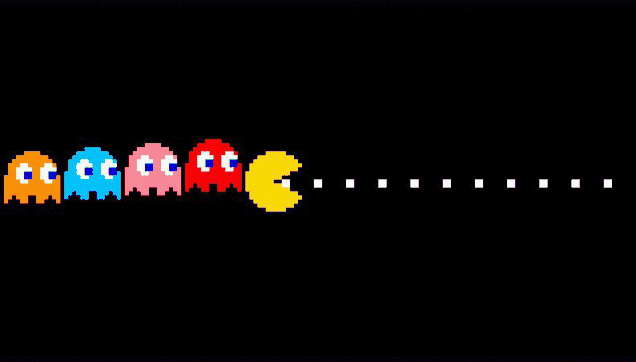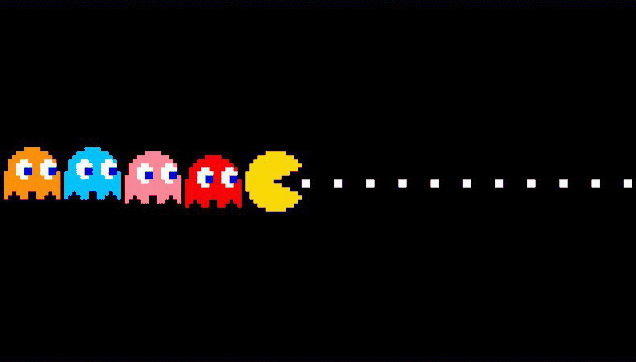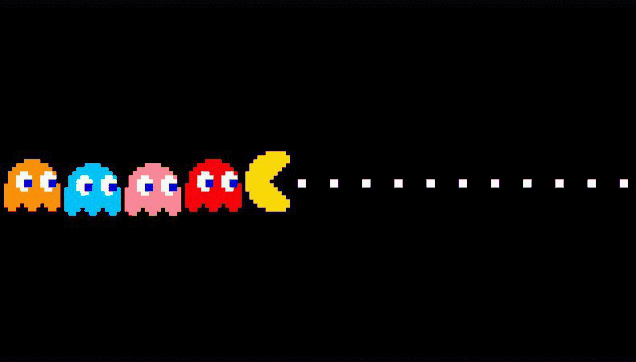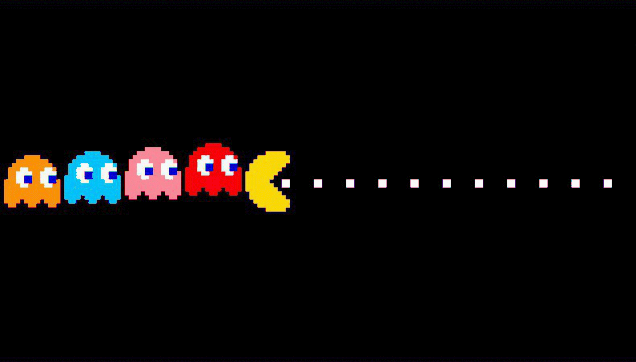 |
| All four Pac-Man Ghosts from the original game, where each had their own strategies of chasing the player. (Grayson. N, 2015) |
' void Chasing ()
{
// Create a vector from the enemy to the last sighting of the player.
Vector3 sightingDeltaPos = enemySight.personalLastSighting - transform.position;
// If the the last personal sighting of the player is not close...
if(sightingDeltaPos.sqrMagnitude > 4f)
// ... set the destination for the NavMeshAgent to the last personal sighting of the player.
nav.destination = enemySight.personalLastSighting;
// Set the appropriate speed for the NavMeshAgent.
nav.speed = chaseSpeed;
// If near the last personal sighting...
if(nav.remainingDistance < nav.stoppingDistance)
{
// ... increment the timer.
chaseTimer += Time.deltaTime;
// If the timer exceeds the wait time...
if(chaseTimer >= chaseWaitTime)
{
// ... reset last global sighting, the last personal sighting and the timer.
lastPlayerSighting.position = lastPlayerSighting.resetPosition;
enemySight.personalLastSighting = lastPlayerSighting.resetPosition;
chaseTimer = 0f;
} Next I will talk about behaviours and neural nets. Behaviours, as sourced from (Simpson.C, 2014), —Behaviours is essentially how AI works. It is sorted through behaviour trees (a high-end graphic modelling language) to model and represent the AI in games. For example different in- game entities in Unity can have different behaviours depending on the situation, such as being idle, patrol, follow, flee, seek, attack, defend, hurt, change, heal, help and dead. A behaviour tree is a tier list that lists nodes in order of importance that decide how an AI entity (such as an NPC) make decisions. The very bottom of the tree (symbolising the leaves) are the actual commands that decide what the NPC does and the branches are different types of nodes that determine how the tree’s AI walks down the tree’s branches to reach the commands of which is best suited to what is happening in-game. An example of a behaviour tree is below.
 |
| An example behaviour tree represented how the decisions are filtered down to different 'leaves'. (Simpson. C, 2014) |
Now onto neutral nets! Which is more of a theory than an implementation of AI. Once again, with information from (TutorialsPoint b, 2015), —Neural nets is the theory of AI almost being human, especially in the future. Where AI will almost become human such as copying the pulses in the brain and how it uses these pulses to tell our bodies commands. Nobody knows exactly what it is, however it tries to simulate how the brain works and emulate the human mind using very advanced technology that learns new things that it experiences throughout its time.






